ورود کاربر (User Login)
در این بخش، نحوه پیادهسازی ورود کاربر (User Login) را بررسی میکنیم. این شامل فرم ورود (Login Form)، احراز هویت (Authentication) و مدیریت نشست (Session Management) میشود.
برای شروع، بیایید یک فرم HTML (HTML Form) برای ورود کاربر (User Login) ایجاد کنیم:
در این فصل قصد داریم روی ایجاد صفحه ورود کاربر برای برنامه خود تمرکز کنیم.
قبل از اینکه به بخش اصلی این کار بپردازیم، بیایید به سرعت به بسته internal/validator که قبلاً ساختهایم نگاهی بیندازیم و آن را بهروزرسانی کنیم تا از خطاهای اعتبارسنجی که به یک فیلد خاص فرم مرتبط نیستند پشتیبانی کند.
ما از این بعداً در فصل استفاده خواهیم کرد تا به کاربر یک پیام عمومی "آدرس ایمیل یا رمز عبور شما اشتباه است" نشان دهیم اگر ورود آنها ناموفق باشد، زیرا این کار امنتر از بیان صریح دلیل شکست ورود است.
لطفاً فایل internal/validator/validator.go خود را به صورت زیر بهروزرسانی کنید:
package validator ... // Add a new NonFieldErrors []string field to the struct, which we will use to // hold any validation errors which are not related to a specific form field. type Validator struct { NonFieldErrors []string FieldErrors map[string]string } // Update the Valid() method to also check that the NonFieldErrors slice is // empty. func (v *Validator) Valid() bool { return len(v.FieldErrors) == 0 && len(v.NonFieldErrors) == 0 } // Create an AddNonFieldError() helper for adding error messages to the new // NonFieldErrors slice. func (v *Validator) AddNonFieldError(message string) { v.NonFieldErrors = append(v.NonFieldErrors, message) } ...
بعد، بیایید یک قالب جدید ui/html/pages/login.tmpl ایجاد کنیم که حاوی نشانهگذاری برای صفحه ورود ما باشد. ما از همان الگوی نمایش خطاهای اعتبارسنجی و نمایش مجدد دادهها که برای صفحه ثبتنام خود استفاده کردیم، پیروی خواهیم کرد.
$ touch ui/html/pages/login.tmpl
{{define "title"}}Login{{end}}
{{define "main"}}
<form action='/user/login' method='POST' novalidate>
<!-- Notice that here we are looping over the NonFieldErrors and displaying
them, if any exist -->
{{range .Form.NonFieldErrors}}
<div class='error'>{{.}}</div>
{{end}}
<div>
<label>Email:</label>
{{with .Form.FieldErrors.email}}
<label class='error'>{{.}}</label>
{{end}}
<input type='email' name='email' value='{{.Form.Email}}'>
</div>
<div>
<label>Password:</label>
{{with .Form.FieldErrors.password}}
<label class='error'>{{.}}</label>
{{end}}
<input type='password' name='password'>
</div>
<div>
<input type='submit' value='Login'>
</div>
</form>
{{end}}
سپس به فایل cmd/web/handlers.go خود بروید و یک ساختار جدید userLoginForm ایجاد کنید (برای نمایش و نگهداری دادههای فرم)، و handler userLogin خود را برای نمایش صفحه ورود تطبیق دهید.
به این صورت:
package main ... // Create a new userLoginForm struct. type userLoginForm struct { Email string `form:"email"` Password string `form:"password"` validator.Validator `form:"-"` } // Update the handler so it displays the login page. func (app *application) userLogin(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { data := app.newTemplateData(r) data.Form = userLoginForm{} app.render(w, r, http.StatusOK, "login.tmpl", data) } ...
اگر برنامه را اجرا کنید و به https://localhost:4000/user/login بروید، اکنون باید صفحه ورود را به این شکل ببینید:
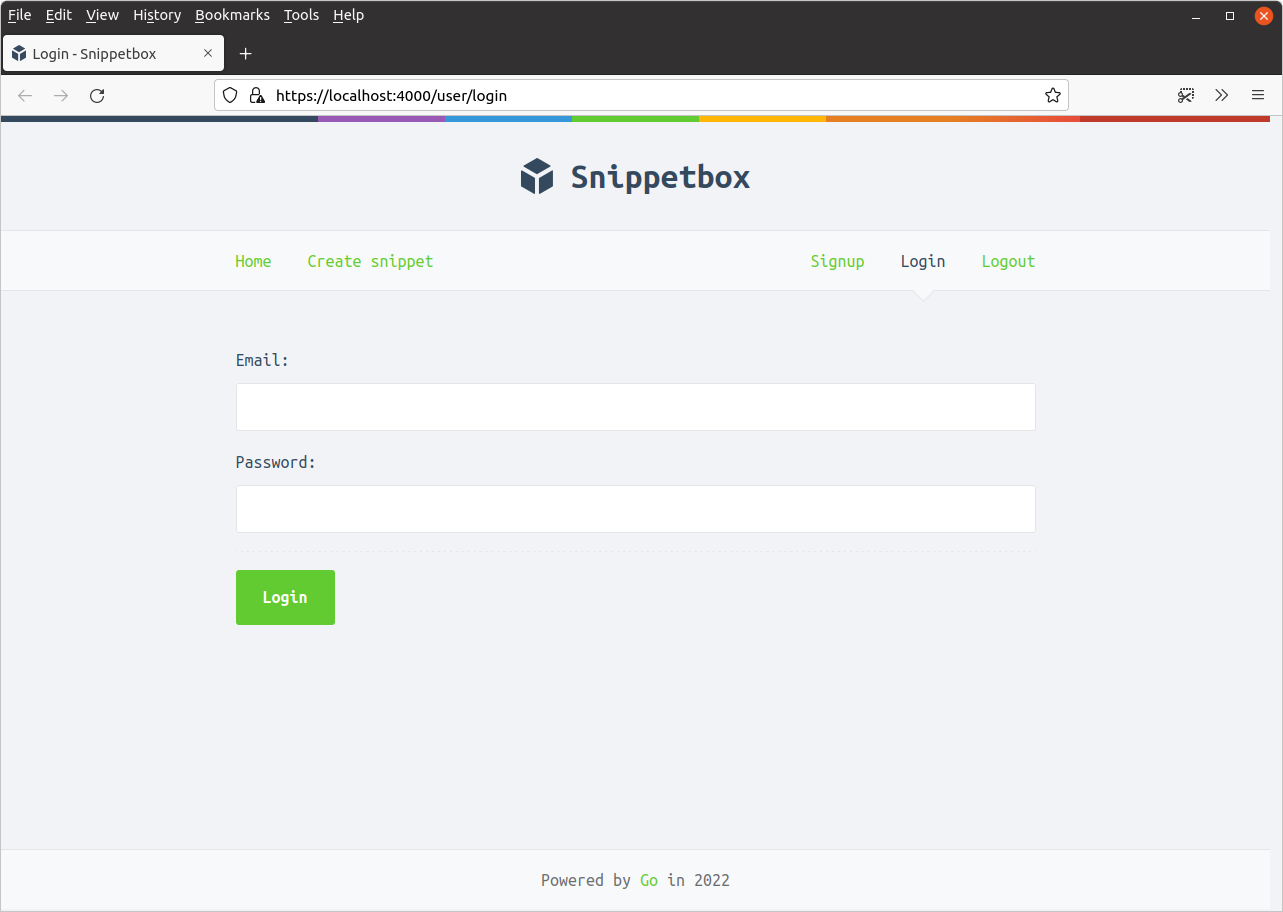
تأیید جزئیات کاربر
گام بعدی بخش جالب است: چگونه میتوانیم تأیید کنیم که ایمیل و رمز عبور ارسال شده توسط کاربر صحیح است؟
بخش اصلی این منطق تأیید در متد UserModel.Authenticate() مدل کاربر ما انجام خواهد شد. به طور خاص، ما به دو چیز نیاز داریم:
ابتدا باید رمز عبور هش شده مرتبط با آدرس ایمیل را از جدول MySQL
usersبازیابی کنیم. اگر ایمیل در پایگاه داده وجود نداشته باشد، خطایErrInvalidCredentialsرا که قبلاً ساختهایم برمیگردانیم.در غیر این صورت، میخواهیم رمز عبور هش شده از جدول
usersرا با رمز عبور متنی که کاربر هنگام ورود ارائه کرده است مقایسه کنیم. اگر آنها مطابقت نداشته باشند، میخواهیم دوباره خطایErrInvalidCredentialsرا برگردانیم. اما اگر مطابقت داشته باشند، میخواهیم مقدارidکاربر را از پایگاه داده برگردانیم.
بیایید دقیقاً این کار را انجام دهیم. کد زیر را به فایل internal/models/users.go خود اضافه کنید:
package models ... func (m *UserModel) Authenticate(email, password string) (int, error) { // Retrieve the id and hashed password associated with the given email. If // no matching email exists we return the ErrInvalidCredentials error. var id int var hashedPassword []byte stmt := "SELECT id, hashed_password FROM users WHERE email = ?" err := m.DB.QueryRow(stmt, email).Scan(&id, &hashedPassword) if err != nil { if errors.Is(err, sql.ErrNoRows) { return 0, ErrInvalidCredentials } else { return 0, err } } // Check whether the hashed password and plain-text password provided match. // If they don't, we return the ErrInvalidCredentials error. err = bcrypt.CompareHashAndPassword(hashedPassword, []byte(password)) if err != nil { if errors.Is(err, bcrypt.ErrMismatchedHashAndPassword) { return 0, ErrInvalidCredentials } else { return 0, err } } // Otherwise, the password is correct. Return the user ID. return id, nil }
گام بعدی ما شامل بهروزرسانی handler userLoginPost است تا دادههای فرم ورود ارسال شده را تجزیه کند و این متد UserModel.Authenticate() را فراخوانی کند.
اگر جزئیات ورود معتبر باشند، سپس میخواهیم id کاربر را به دادههای جلسه آنها اضافه کنیم تا — برای درخواستهای آینده — بدانیم که آنها با موفقیت احراز هویت شدهاند و کدام کاربر هستند.
به فایل handlers.go خود بروید و آن را به صورت زیر بهروزرسانی کنید:
package main ... func (app *application) userLoginPost(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { // Decode the form data into the userLoginForm struct. var form userLoginForm err := app.decodePostForm(r, &form) if err != nil { app.clientError(w, http.StatusBadRequest) return } // Do some validation checks on the form. We check that both email and // password are provided, and also check the format of the email address as // a UX-nicety (in case the user makes a typo). form.CheckField(validator.NotBlank(form.Email), "email", "This field cannot be blank") form.CheckField(validator.Matches(form.Email, validator.EmailRX), "email", "This field must be a valid email address") form.CheckField(validator.NotBlank(form.Password), "password", "This field cannot be blank") if !form.Valid() { data := app.newTemplateData(r) data.Form = form app.render(w, r, http.StatusUnprocessableEntity, "login.tmpl", data) return } // Check whether the credentials are valid. If they're not, add a generic // non-field error message and re-display the login page. id, err := app.users.Authenticate(form.Email, form.Password) if err != nil { if errors.Is(err, models.ErrInvalidCredentials) { form.AddNonFieldError("Email or password is incorrect") data := app.newTemplateData(r) data.Form = form app.render(w, r, http.StatusUnprocessableEntity, "login.tmpl", data) } else { app.serverError(w, r, err) } return } // Use the RenewToken() method on the current session to change the session // ID. It's good practice to generate a new session ID when the // authentication state or privilege levels changes for the user (e.g. login // and logout operations). err = app.sessionManager.RenewToken(r.Context()) if err != nil { app.serverError(w, r, err) return } // Add the ID of the current user to the session, so that they are now // 'logged in'. app.sessionManager.Put(r.Context(), "authenticatedUserID", id) // Redirect the user to the create snippet page. http.Redirect(w, r, "/snippet/create", http.StatusSeeOther) } ...
بسیار خوب، بیایید این را امتحان کنیم!
برنامه را مجدداً راهاندازی کنید و سعی کنید برخی از اعتبارنامههای کاربر نامعتبر را ارسال کنید…
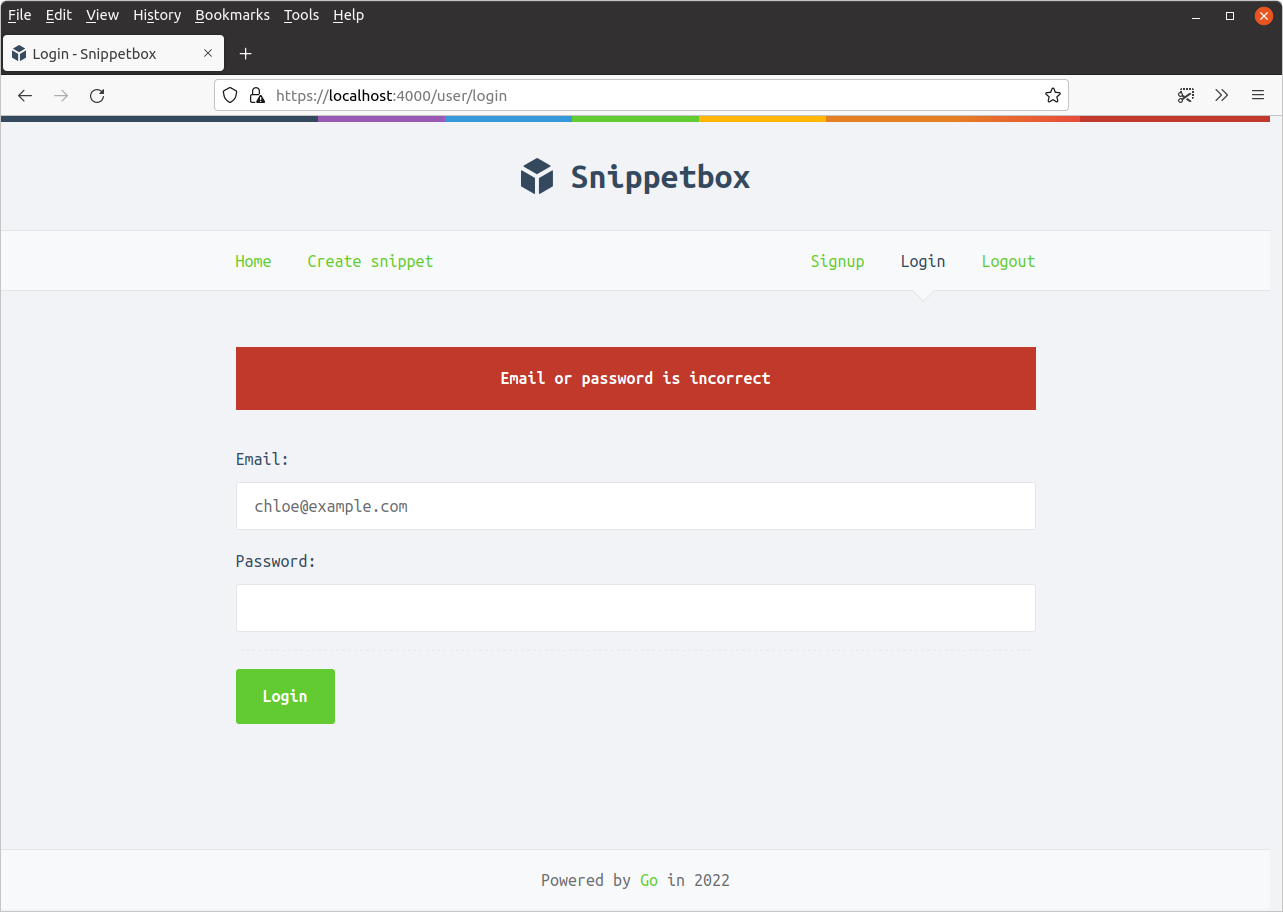
باید یک پیام خطای اعتبارسنجی غیر فیلدی دریافت کنید که به این شکل است:
اما وقتی برخی از اعتبارنامههای صحیح را وارد میکنید (از آدرس ایمیل و رمز عبور برای کاربری که در فصل قبلی ایجاد کردهاید استفاده کنید)، برنامه باید شما را وارد کند و به صفحه ایجاد قطعه هدایت کند، به این صورت:
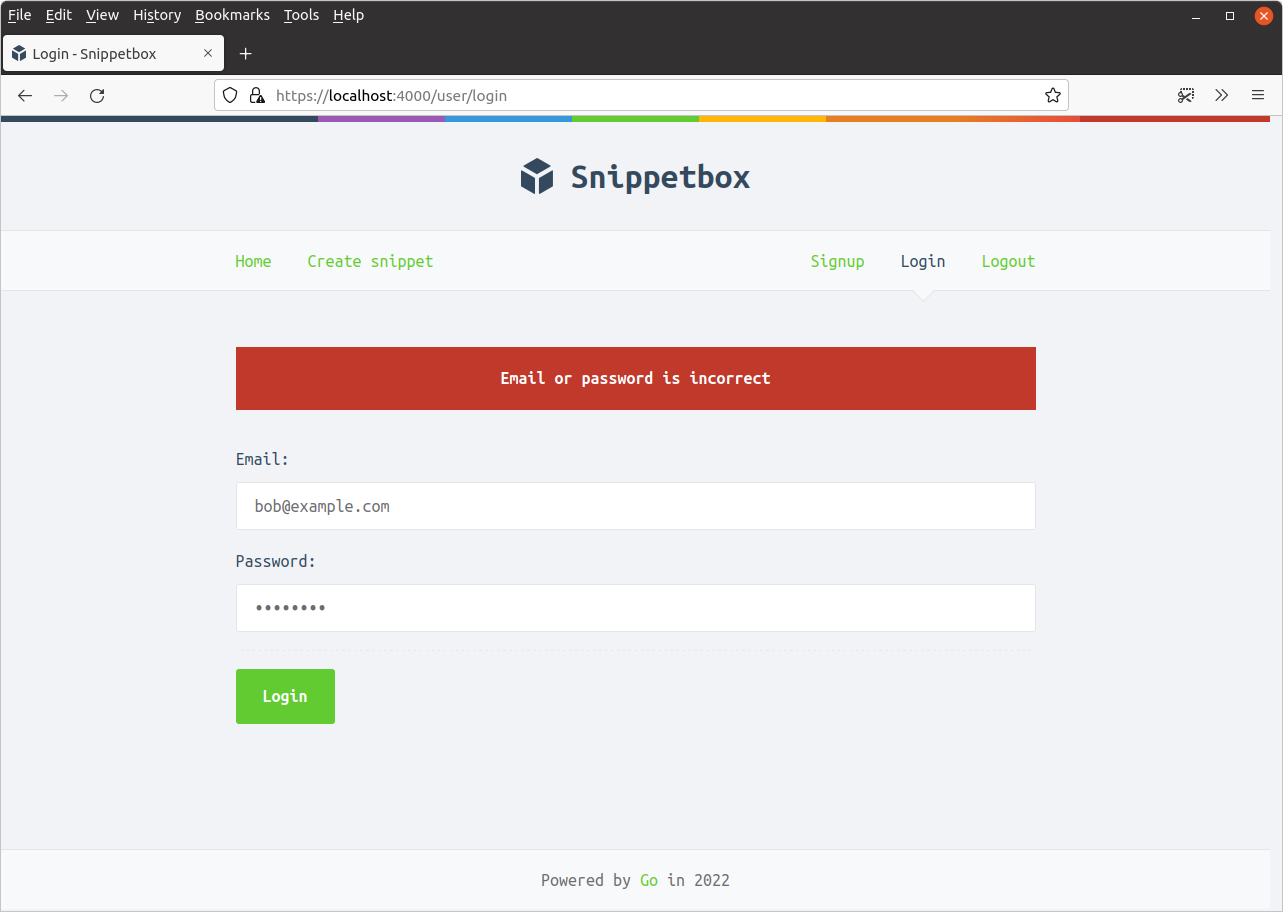
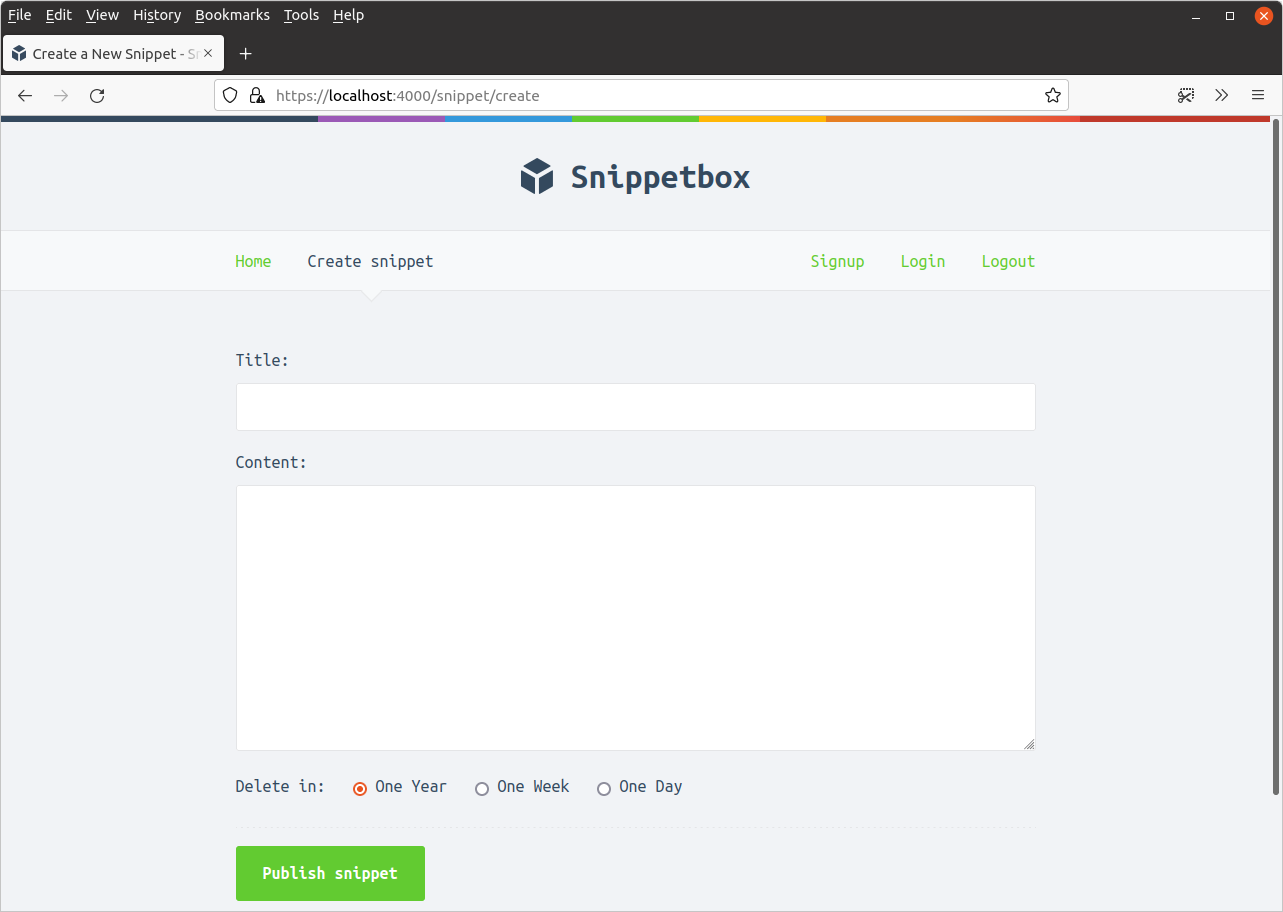
ما در دو فصل گذشته کارهای زیادی انجام دادهایم، بنابراین بیایید به سرعت بررسی کنیم که وضعیت چگونه است.
کاربران اکنون میتوانند با استفاده از فرم
GET /user/signupدر سایت ثبتنام کنند. ما جزئیات کاربران ثبتنام شده (از جمله نسخه هش شده رمز عبور آنها) را در جدولusersپایگاه داده خود ذخیره میکنیم.کاربران ثبتنام شده سپس میتوانند با استفاده از فرم
GET /user/loginبرای ارائه آدرس ایمیل و رمز عبور خود احراز هویت کنند. اگر این موارد با جزئیات یک کاربر ثبتنام شده مطابقت داشته باشد، ما آنها را به عنوان احراز هویت موفقیتآمیز میدانیم و مقدار"authenticatedUserID"مربوطه را به دادههای جلسه آنها اضافه میکنیم.
واژهنامه اصطلاحات فنی
| اصطلاح فارسی | معادل انگلیسی | توضیح |
|---|---|---|
| ورود کاربر | User Login | فرآیند دسترسی به حساب کاربری |
| فرم ورود | Login Form | فرم ورود اطلاعات کاربر |
| احراز هویت | Authentication | تأیید هویت کاربر |
| مدیریت نشست | Session Management | کنترل نشستهای کاربری |
| فرم HTML | HTML Form | فرم ورود اطلاعات |
| اعتبارسنجی | Validation | بررسی صحت اطلاعات |
| رمز عبور | Password | کلمه عبور کاربر |
| کوکی نشست | Session Cookie | کوکی نگهداری اطلاعات نشست |
| خطای ورود | Login Error | پیام خطای ورود ناموفق |
| امنیت | Security | حفاظت از حساب کاربری |